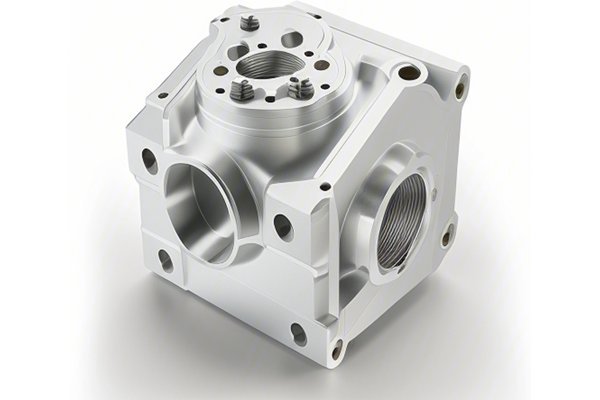
Opening: A World of Precision at Our Fingertips
Did you know that the global CNC machining market is projected to reach $117.93 billion by 2026? This growth is rooted in the increasing demand for precision and efficiency across various industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical technology. But amid this technological evolution, the terms “CNC machining” and “precision machining” often get thrown around interchangeably, leading to confusion in both manufacturing circles and among potential clients. So, what really distinguishes CNC machining from precision machining? In this extensive blog post, we’ll demystify these concepts, delve into their unique advantages, applications, and much more.
Defining CNC Machining
What is CNC Machining?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is an advanced manufacturing process that uses computers to control machine tools for precise configuration and execution of manufacturing tasks. This method allows for improved accuracy, efficiency, and repeatability compared to traditional machining techniques.
Core Technologies in CNC Machining
Advantages of CNC Machining
Defining Precision Machining
What is Precision Machining?
Precision machining refers to the processes that achieve finely-tuned specifications, where the tolerances are extremely tight (often within a few microns). It encompasses various forms of machining including CNC machining but focuses specifically on the level of accuracy and precise control that is achieved.
Core Technologies in Precision Machining
Advantages of Precision Machining
Key Differences Between CNC Machining and Precision Machining
Common Misconceptions
CNC Machining is Always More Accurate
One of the prevalent misconceptions is that CNC machining is inherently more accurate than any other form of machining. While CNC machines can be remarkably precise, the distinction lies in the goal of the operation rather than the machinery itself. Both CNC and precision machining can yield excellent results, but the choice between them depends on the requirements of the job at hand.
Precision Machining is Outdated
Although precision machining has been around longer than CNC, with advancements in technology and tooling, it remains relevant and frequently employed in industries requiring exact specifications.
Applications of CNC and Precision Machining
Applications of CNC Machining
Applications of Precision Machining
How to Choose Between CNC and Precision Machining
When determining which option is best for your manufacturing needs, consider these factors:
: The Crucial Decision in Manufacturing
In the landscape of modern manufacturing, understanding the difference between CNC machining and precision machining is vital. While both practices serve distinct roles—CNC machining flourishing in its ability to streamline production and precision machining excelling in producing intricately engineered components—they each contribute to the greater goal of quality manufacturing.
With industries and technologies evolving rapidly, staying informed about such differences enables business leaders and manufacturing professionals to make knowledgeable choices about their production processes.
So, as we look towards the future of manufacturing, remember that the choice of machining method can play a pivotal role in the success of your projects. Whether you’re optimizing production costs or striving for unparalleled accuracy, recognizing the strengths of both CNC and precision machining can set your business in the right direction.
Stay curious, stay engaged, and keep pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in manufacturing!






