Did you know that approximately 30% of the total production costs in CNC machining can be attributed not only to the material itself but primarily to post-processing activities? This staggering statistic highlights the significant role post-processing plays in the overall success of CNC prototypes. As a key part of the manufacturing process, understanding these post-processing steps can mean the difference between a successful prototype and one that fails to meet its intended purpose.
Understanding CNC Prototyping
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) prototyping is a modern manufacturing method that leverages cutting-edge technology to precisely shape materials into prototypes. One of the critical aspects that set CNC apart from traditional machining is its ability to produce intricately detailed designs with high accuracy. However, the fabrication of a physical prototype is only part of the equation; post-processing plays an indispensable role in perfecting the finish, functionality, and overall quality of these parts.
What is Post-Processing?
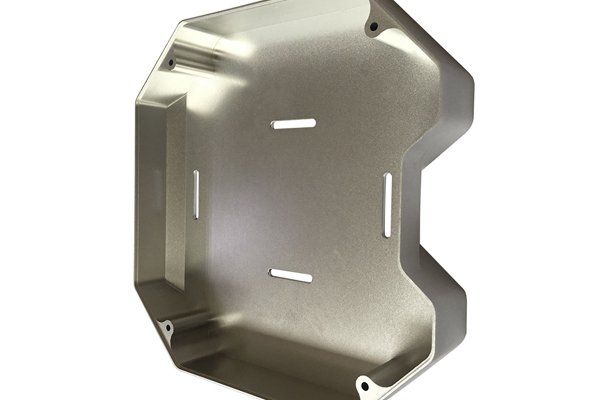

Post-processing refers to the various processes applied after the initial CNC machining operations to enhance or finalize a prototype. These processes can vary depending on the material, the application of the prototype, and the desired finish but may include operations such as sanding, polishing, coating, heat treatment, deburring, and more.
Key Post-Processing Techniques
Understanding post-processing is essential for maximizing the quality and performance of CNC prototypes. Below, we’ve broken down some of the most common post-processing techniques, their purposes, and how they can be efficiently implemented.
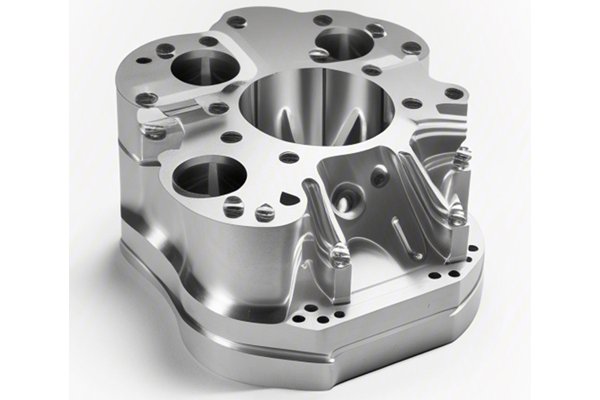

Deburring is the process of removing sharp edges or burrs that can form during machining. Burrs not only affect the aesthetic quality but can also impact the functional aspects of a prototype, such as fit and safety. Effective deburring can involve various methods:
Achieving the desired surface finish is critical for aesthetic and functional purposes. Sanding involves the removal of material to even out the surface, while polishing is a more refined process aimed at creating a high shine.
Coating refers to various methods of applying a protective or functional layer to the surface of the prototype. This can serve multiple purposes, including aesthetic enhancement, corrosion resistance, and overall durability.
Heat treatment processes can modify the mechanical properties of metals and plastics. This may involve processes like annealing, hardening, or tempering to develop desired qualities such as increased strength, flexibility, or thermal resistance.
Beyond polishing, several specialized finishing techniques exist to improve surface properties:
The Importance of Choosing the Right Processes
Selecting the right post-processing techniques is crucial. Factors such as material type, design complexity, intended application, and expected lifecycle all play significant roles in determining the appropriate post-processing strategy.
The journey of CNC prototypes does not end with machining; post-processing is essential to achieving the necessary specifications and quality. Techniques like deburring, sanding, polishing, coating, and heat treatment are vital to transforming a machined piece into a fully functional prototype. Post-processing not only enhances the quality and performance of a prototyped part but can also significantly impact its success in the marketplace.
As manufacturing continues to evolve, understanding and implementing effective post-processing techniques will remain a necessity. It’s not just about creating prototypes; it’s about ensuring they serve their intended purpose meticulously and efficiently. For engineers, designers, and manufacturers, taking the time to understand these processes can lead to higher quality products, lower production costs, and increased customer satisfaction—demonstrating why this blog is both important and worth your consideration.




