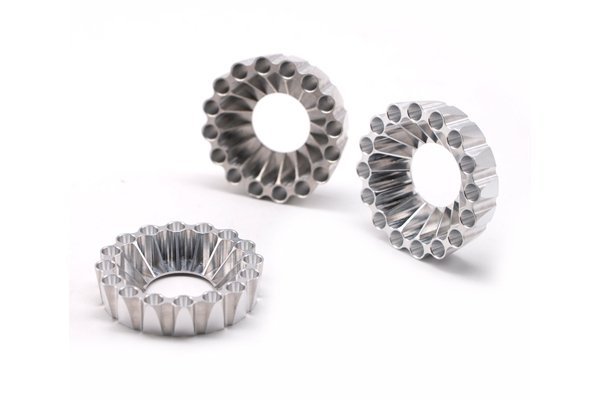
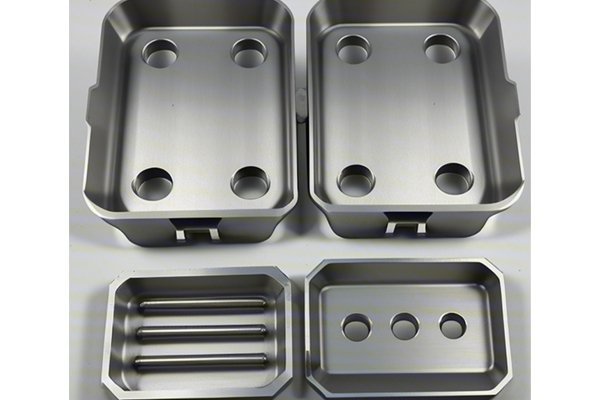
Did you know that the global CNC machining market is projected to reach $100 billion by 2024, growing at a rate of over 6% annually? This impressive growth highlights the increasing reliance on CNC machining across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and medical devices. As the demand for precision-engineered components continues to rise, it becomes essential to understand the various machining processes available, particularly the differences between plastic CNC machining and metal machining plasticity.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the fundamental distinctions between these two machining methods, exploring the materials used, processes involved, and the advantages and disadvantages of each. Whether you’re a manufacturer, engineer, or simply someone interested in CNC machining, understanding these differences can lead to better decision-making and enhanced production quality.
Understanding CNC Machining
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a manufacturing process that employs pre-programmed computer software to control machinery. This automated process allows for high precision and repeatability, as machines can operate continuously with minimal oversight. CNC machining can work with multiple materials, including metals and plastics, allowing manufacturers to create intricate parts and components with great accuracy.
The Role of Plastic in CNC Machining
Plastics are increasingly being used in engineering applications due to their versatility, lightweight properties, and resistance to corrosion. Standard plastics, such as ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) and polycarbonate, are commonly machined using CNC technology. These materials are particularly beneficial in industries that require non-metal components, such as medical devices and consumer goods.
Metal Machining Plasticity Explained
On the other hand, metal machining plasticity deals with the behavior of metals when they are subjected to stresses and deformations. Metals like aluminum, steel, and titanium exhibit plastic deformation characteristics, which means they can be reshaped under pressure without breaking. This feature is crucial in various applications, particularly in creating high-strength components for construction and heavy machinery.
Key Differences Between Plastic CNC Machining and Metal Machining Plasticity
Let’s explore the primary distinctions between plastic CNC machining and metal machining plasticity, which will guide you in choosing the right process for your specific requirements.
Plastic Machining:
Metal Machining:
The actual process of CNC machining differs for plastics and metals due to material characteristics:
Plastic CNC Machining:
Metal Machining:
The applications of plastic and metal CNC machining vary widely:
Plastic Machining Applications:
Metal Machining Applications:
When conducting CNC machining operations, cost-effectiveness plays a crucial role:
Plastic CNC Machining:
Metal Machining:
Advantages and Disadvantages
Understanding the pros and cons of each machining type is essential for making an informed choice.
Advantages of Plastic CNC Machining
Disadvantages of Plastic CNC Machining
Advantages of Metal Machining
Disadvantages of Metal Machining
Decision-Making: Choosing the Right Machining Process
Now that you have a clearer understanding of the differences between plastic CNC machining and metal machining plasticity, how can you determine which process is right for your project? Here are some key considerations:
Understand the specific requirements of your application, including:
Conduct a thorough cost analysis, considering:
Evaluate the role of prototyping in your project:
As industries across the globe continue to evolve, understanding the distinctions between plastic CNC machining and metal machining plasticity is essential for engineers and manufacturers alike. The selection of materials can significantly impact the performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness of components used across various applications.
In summary, plastic machining is ideal for applications requiring lightweight and corrosion-resistant parts, while metal machining is preferable when strength and durability are paramount. By considering the key differences, advantages, and limitations outlined in this blog post, companies can make well-informed decisions that enhance their manufacturing processes and ultimately improve product quality.
As technology progresses and new materials are developed, maintaining a mindset of continuous learning will empower manufacturers to embrace innovative solutions for their machining needs. In the fast-paced world of CNC machining, understanding your options and effectively leveraging them can provide a competitive advantage worth thinking about. Whether you’re deciding how to streamline production or exploring new materials, remembering the nuances discussed in this article can steer your project toward success.






