: An Eye-Opening Statistic
Did you know that nearly 90% of manufacturers report challenges in meeting customer demands for precision and quality in prototype production? That’s a staggering figure that reflects the growing complexity of manufacturing in today’s fast-paced environment. As industries evolve, the need for precision metal prototypes has never been greater. Enter CNC machining with 5th axis technology, a game-changer that not only enhances precision but also accelerates production times.
In this comprehensive blog post, we will delve deep into the intricacies of CNC machining for precision metal prototypes, especially focusing on the advantages offered by 5th axis technology. By the end of this article, you will have a firm grasp of why investing in these advanced techniques is essential for maintaining competitiveness and excellence in the manufacturing sector.
Section 1: Understanding CNC Machining
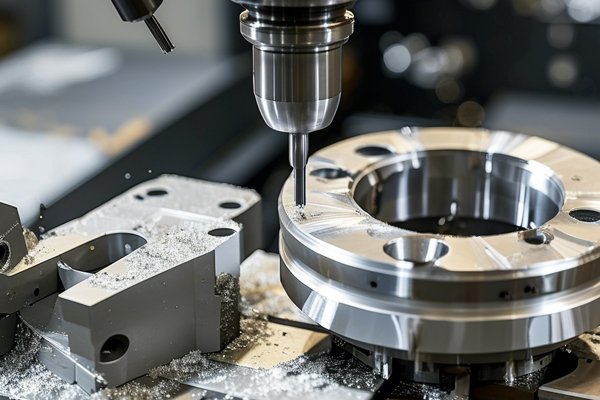

1.1 What is CNC Machining?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that uses computerized controls to guide machine tools in performing various manufacturing tasks. Unlike traditional methods, CNC machining allows for remarkable levels of precision, often achieving tolerances within a thousandth of an inch. This capability has made CNC machining a fundamental process across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical equipment, and more.
1.2 The Basics of 5th Axis Machining
While 3-axis and 4-axis machining is standard, the introduction of 5th axis machining enhances its capabilities. But what does “5th axis” mean? Essentially, it refers to the ability of a CNC machine to rotate on an additional axis, allowing for more complex geometries and intricately detailed parts without requiring the workpiece to be repositioned.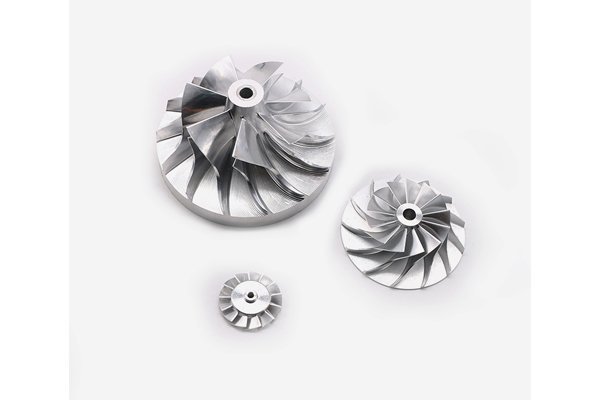
1.3 Key Components of CNC Machines
For CNC machining to operate efficiently, it typically consists of several key components:
Understanding these components lays the groundwork for appreciating the intricacies of CNC machining.
Section 2: The Advantages of CNC Machining
2.1 Enhanced Precision and Accuracy
One of the most significant advantages of CNC machining is its precision. Traditional machining processes rely heavily on human skill – a variable that can introduce errors. In contrast, CNC machines operate based on digital instructions, providing consistency and high precision sizes.
2.2 Increased Efficiency and Speed
CNC machining dramatically boosts efficiency compared to manual processes. The ability to run multiple parts in a cycle, combined with the capability to automate operations, means that manufacturers can shorten lead times while producing large batches.
2.3 Design Flexibility and Complexity
CNC machines are crucial for creating intricate designs that would be challenging or impossible to achieve manually. 5th axis machining, in particular, allows for multi-dimensional shapes and undercuts, substantially improving design flexibility for engineers.
Section 3: The Role of 5th Axis Technology in CNC Machining
3.1 Definition and Functionality
As mentioned earlier, 5th axis machining expands on the capabilities of traditional CNC machining by adding an additional rotational axis. This added movement, along the X, Y, Z, and A axes, allows for greater complexity in machining operations.
3.2 Advancements in 5th Axis Technology
Modern CNC machines equipped with 5th axis capability come with advanced features, including:
3.3 Case Studies: Real-World Applications
Section 4: Common Challenges in CNC Machining and Solutions
4.1 Tool Wear and Maintenance
Problem:
With extensive use, tools can wear down, affecting the quality of the machining process.
Solution:
Implementing a predictive maintenance schedule and using high-quality tooling materials can prevent excessive wear and extend tool life. Additionally, using tool wear sensors can mitigate this issue.
4.2 Programming Complexity
Problem:
As designs become more intricate, programming for CNC machines can pose difficulties.
Solution:
Adopting user-friendly CNC programming software with simulation capabilities can aid operators in avoiding mistakes. Furthermore, thorough training programs can enhance operators’ proficiency, minimizing errors during programming.
4.3 Cost-Effectiveness
Problem:
High initial costs associated with CNC machinery and tooling can be a barrier to entry for some companies.
Solution:
Though these costs can be daunting, they often yield significant long-term savings in terms of reduced labor and increased efficiency. Conducting a cost-benefit analysis can help businesses visualize their ROI effectively.
Section 5: Best Practices for CNC Machining with 5th Axis Technology
5.1 Designing for Manufacturability
When creating designs, it’s crucial to remember the capabilities and limitations of CNC machining. Designs that consider ease of machining can drastically reduce lead times and costs.
5.2 Regular Calibration and Maintenance
Regular machine calibration helps maintain accuracy across various operations. Combining this with a vigilant maintenance regime ensures machines serve their purpose efficiently.
5.3 Investing in Employee Training
Having highly skilled employees who fully understand CNC operations can optimize machine usage and reduce production errors. Continued education and training should be integral parts of any organization’s strategy.
Section 6: Future Trends in CNC Machining
6.1 Industry 4.0 and Smart Machining
With the rise of Industry 4.0, CNC machines are becoming increasingly interconnected. This technology allows for enhanced monitoring of production processes and real-time data analysis, further improving efficiencies.
6.2 Artificial Intelligence Integration
The incorporation of AI in CNC machining can lead to smarter operations and decision-making processes, optimizing production schedules based on demand forecasting.
6.3 Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
Sustainability is becoming a core value in manufacturing. Companies are focusing on reducing waste and energy consumption through lean techniques and efficient machining strategies.
: Crafting the Future with Precision Technology
In conclusion, CNC machining, especially with the integration of 5th axis technology, offers unparalleled advantages for producing precision metal prototypes. From enhanced accuracy to increased production efficiency, these advanced machining methods are integral for companies aiming to stay competitive in demanding markets.
Manufacturing is continually evolving, and understanding the principles of CNC machining will better equip businesses to tackle tightening tolerances and complex designs. As you consider the implications of this technology, it’s crucial to recognize its significant role in shaping the future of manufacturing.
Why You Should Care
Investing in CNC machining technology is not merely a financial decision; it’s a strategic one that impacts a business’s capability to innovate and respond to market needs. As industries increasingly turn towards automation and precision, companies that adapt to and embrace these advancements will not only survive but thrive. Therefore, empowering yourself with this knowledge can position you to lead in the manufacturing landscape of tomorrow.




