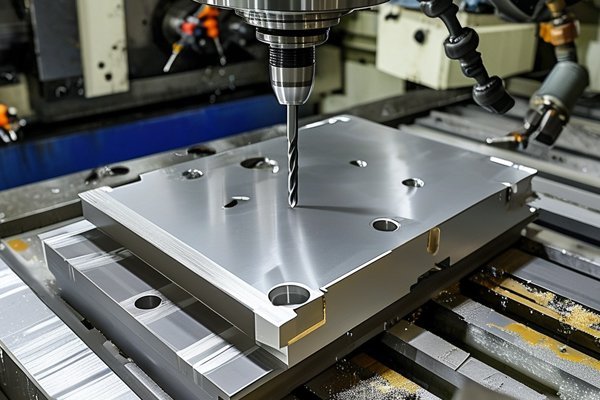
Did you know that the global CNC machining market is expected to reach $100 billion by 2025? This staggering statistic illustrates the growing importance of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining in modern manufacturing. As industries continue to evolve, the need for precision, efficiency, and adaptability has never been higher. CNC machining serves as a backbone for many sectors, from aviation to healthcare, but not all CNC methods are created equal. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, along with specific scenarios where it shines or falls short. In this comprehensive blog, we will dive into the various CNC machining methods, weigh their pros and cons, and provide guidance on when to use each technique.
What is CNC Machining?
CNC machining is a manufacturing process that utilizes computer-controlled equipment to produce parts and components with high precision. In contrast to traditional machining methods that rely on manual operations, CNC machining automates the entire process, enabling faster production cycles, increased accuracy, and repeatability.
Brief History and Evolution
CNC machining has its roots in the early 20th century, originally using punched tape to control machine tools. Over the decades, this technology has evolved into sophisticated systems that include advanced software and multi-axis machines. Today, CNC machining is ubiquitous in various industries, enabling innovation in product design and manufacturing.
CNC Milling
CNC milling is a subtractive manufacturing process where rotary cutters remove material from a workpiece. It is one of the most versatile CNC machining methods, suitable for various materials such as metals, plastics, and wood.
CNC Turning
In CNC turning, a rotating workpiece is machined while stationary cutting tools shape it. This method is ideal for producing cylindrical parts, such as shafts and fittings.
CNC Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
EDM is a non-traditional machining process that uses electrical discharges (sparks) to erode material from a workpiece, allowing for intricate designs and hard materials to be shaped accurately.
CNC Laser Cutting
CNC laser cutting employs a high-powered laser beam to cut through materials. It offers exceptional precision and speed and is commonly used in the automotive and aerospace industries.
CNC Waterjet Cutting
Using high-pressure water to cut through materials, CNC waterjet cutting is effective for creating complex shapes in various materials, including metals, ceramics, and plastics without introducing heat-affected zones.
Precision and Accuracy
One of the most significant benefits of CNC machining is its ability to produce parts with extreme accuracy. CNC systems can achieve tolerances within ±0.005 inches or better, making them ideal for tight tolerances in industries like aerospace and medical devices.
Versatility in Material Types
CNC machining is not limited to a specific type of material. It can handle metals, plastics, composites, and even wood, making it suitable for a wide range of applications across various industries.
Speed of Production
With automation, CNC machines can operate continuously, significantly reducing production times. This speed is crucial for mass production scenarios where time-to-market is a competitive advantage.
Cost-effectiveness
While the initial investment for CNC machines can be high, the long-term return on investment is substantial. The ability to produce complex parts accurately and quickly reduces material waste and labor costs through automation.
Setup Time and Complexity
Setting up CNC machines can take more time compared to traditional methods, especially for more complex parts. This setup period can lead to higher costs and prolong project timelines.
Initial Investment Costs
Purchasing CNC machinery requires a significant financial commitment, which can be a barrier for small businesses. Additionally, specialized software must also be considered in the overall cost.
Limitations in Material Thickness and Sizes
Certain CNC methods have limitations regarding the thickness and size of materials they can handle. For example, while waterjet cutting can cut thicker materials, CNC milling may be limited to specific dimensions.
Maintenance and Technical Knowledge
CNC machines require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Additionally, skilled operators are needed to program and operate these complex systems, increasing labor costs.
Industries and Applications
Case Studies
When to Use Each CNC Method
Real-world Applications
Each CNC method has its unique applications that cater to specific needs, making it crucial for businesses to understand which method aligns with their manufacturing goals.
In summation, understanding the advantages and disadvantages of various CNC machining methods enables manufacturers to make informed decisions that suit their specific needs. From CNC milling to laser cutting, each method offers unique benefits that can optimize production efficiency and cost-effectiveness. As industries adapt to new technologies, it’s essential to stay informed about which CNC methods can best cater to their evolving manufacturing demands.
This blog serves as a comprehensive guide for both newcomers and seasoned professionals in the manufacturing sector. The insights provided here will not only enhance your understanding of CNC machining but also inspire strategic choices that can drive your business to greater heights. As you consider the future of your manufacturing operations, remember the importance of the right technique and its potential to revolutionize your production processes.






