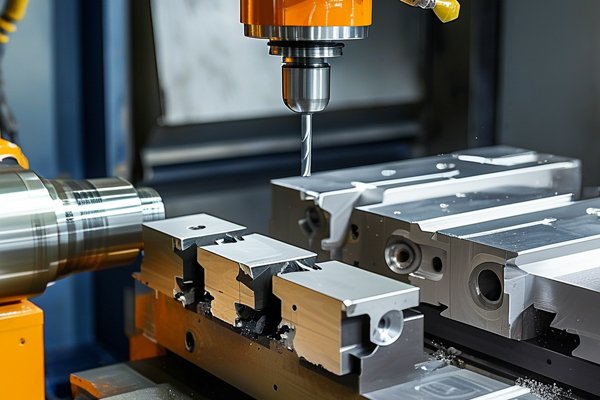
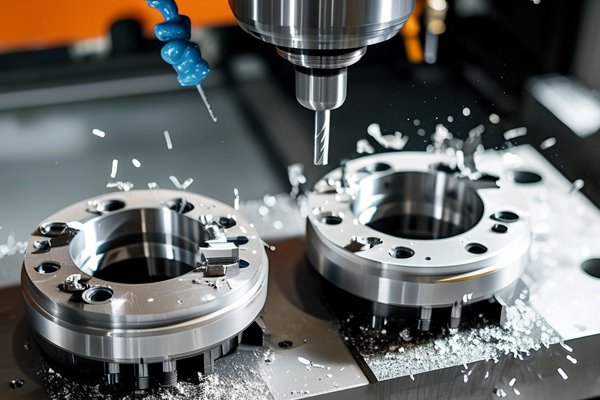
Did you know that over 70% of all industrial metal parts produced today incorporate some form of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) processing? This technology has revolutionized the manufacturing landscape, enabling intricate designs and tolerances that were once thought impossible. Among the various metals employed in CNC machining, aluminum stands out—not just for its lightweight properties and corrosion resistance, but also for its advantageous melting point, which can significantly improve the CNC processing effect when integrated with 3D printing technology.
This blog will delve deep into how the melting point of aluminum can serve as a game-changer in CNC processing, particularly in conjunction with 3D printing. We’re playing a proactive role in exploring not just the technical intricacies involved but also the practical applications, benefits, and the latest advancements in this rapidly evolving sector.
Understanding Aluminum and Its Melting Point
What is Aluminum?
Aluminum is a versatile metal known for its lightweight, durability, and resistance to corrosion. It is the most abundant metal in the earth’s crust and has found applications across numerous industries—from aerospace and automotive to electronics and construction.
Melting Point Significance
The melting point of aluminum is approximately 660°C (1,220°F). This relatively low melting point, compared to other metals like steel, serves multiple advantages in CNC processing. This is especially true when utilizing methods such as metal additive manufacturing, where temperatures can be tightly controlled, thus enhancing the precision of both 3D printing and CNC operations.
Advantages of Aluminum’s Melting Point in CNC Processing
The Intersection of CNC Machining and 3D Printing
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is a groundbreaking technology that fabricates three-dimensional objects from a digital file. This is accomplished layer by layer using various materials, including plastics, metals, and ceramics. Coupling this technology with CNC machining can yield remarkable synergies for manufacturers.
Why Combine CNC Machining with 3D Printing?
Detailed Solutions to Enhance CNC Processing through Aluminum Melting Point
Selecting the appropriate aluminum alloy is crucial. Alloys like Aluminum 6061 or Aluminum 7075 present different melting and thermal characteristics, affecting CNC processing outcomes. Additionally, understanding their machinability can determine how effectively the alloy can be transformed during CNC processes.
Implementing control mechanisms to maintain consistent temperatures is vital. Below are a couple of methods:
In the context of 3D printing, slicing algorithms can be optimized to incorporate the thermal characteristics of aluminum. When combined with CNC machining tool paths, the layer deposition will align with the CNC tool’s cutting paths, leading to fewer errors and increased accuracy.
3D printed aluminum parts often require further refinement via CNC to enhance surface finish and dimensional accuracy. Techniques may include:
Utilizing specialized cutting tools designed explicitly for aluminum can dramatically enhance the CNC process. Here are some recommendations:
Using non-destructive testing (NDT) methods, such as ultrasonic testing or X-ray imaging, ensures that the parts produced through CNC processing meet quality standards and do not have internal flaws—crucial to industries requiring flawless components, such as aerospace.
Industry Applications of Aluminum in CNC and 3D Printing
Discussing the technological advantages of aluminum’s melting point in the context of CNC and 3D printing would be incomplete without illustrating its real-world applications.
Aerospace Sector
Aluminum parts requiring complex aerodynamics are ideally matched with CNC processing. This combination allows for lightweight structures that do not compromise strength.
Automotive Industry
Manufacturers are increasingly looking to aluminum to produce engine components, brackets, and lightweight frameworks through both CNC machining and 3D printing.
Medical Devices
Precision parts, required in medical devices, benefit from the enhanced accuracy and quick turnaround times that the melting point of aluminum enables.
Consumer Electronics
The integration of aluminum components in electronics, created via CNC and 3D processes, leads to smaller, more efficient devices.
The melting point of aluminum serves as a crucial factor that can significantly enhance the CNC processing effect when combined with 3D printing technology. Through optimized alloy selection, advanced tooling, precise temperature control, and adopting innovative techniques, manufacturers can achieve remarkable results.
By understanding these implications and solutions, you can better appreciate this intersection of technologies and how they are reshaping the future of manufacturing.
As industries continue to evolve, the ability to effectively utilize the unique properties of materials like aluminum will play a fundamental role in sustaining progress. It’s essential to remain engaged, consider these strategies, and keep exploring the advances in CNC and 3D printing technologies. The future is bright, and now is the time to shape it.






