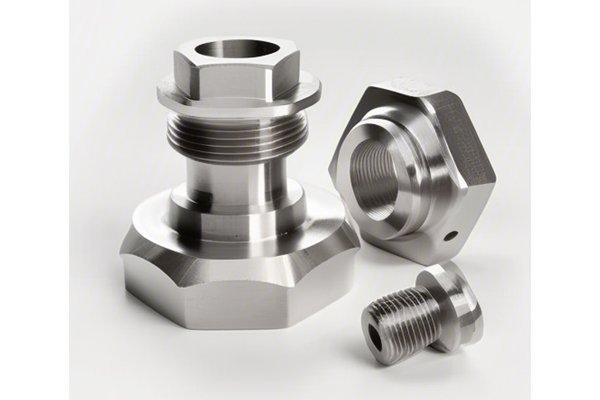
Did you know that brass is an alloy primarily composed of copper and zinc, and its melting point can range anywhere from 900 to 940 degrees Celsius (1652 to 1724 degrees Fahrenheit) depending on its composition? This characteristic significantly influences not only the casting process but also the CNC machining of brass components. As industries demand increased precision and efficiency in manufacturing processes, understanding the relationship between melted brass properties and CNC machining becomes vital for engineers, manufacturers, and designers.
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, the success of CNC machined brass parts heavily relies on a thorough understanding of material properties, particularly the effects of melting points during the machining process. This blog will deep dive into the crucial relationship between melted brass characteristics and CNC machining and detail effective solutions to optimize part quality and efficiency.
Understanding Brass and Its Properties
What is Brass?
Brass is an alloy made mainly of copper and zinc, and it is prized for its malleability, corrosion resistance, and attractive yellow-gold appearance. Various grades of brass exist, each with distinct properties tailored to meet specific industrial needs. For example, C36000 (or Free-Cutting Brass) is commonly used in the manufacturing of precision-machined parts because of its superior machinability.
Key Properties of Brass
The Relationship Between Melting Point and CNC Machining
Melting Point Dynamics
The melting point of brass affects its behavior during both casting and CNC machining. If brass is heated above its melting point but not cooled properly, it can suffer from various issues such as reduced mechanical strength or warping during the cooling phase. Thus, understanding the melting point helps determine the best conditions for CNC machining.
Effect on Machining Processes
Optimizing CNC Machining of Brass
Matched Tooling
Selecting the appropriate tools made of materials that can withstand high temperatures and friction is vital. Carbide tools are typically recommended because they can handle the thermal stresses better and last longer when machining brass.
Cooling Systems
Using effective cooling mechanisms, like coolant fluids or air jets, during CNC machining is crucial for maintaining the temperature, preventing the brass from reaching its melting point, and ensuring prolonged tool life.
Proper Speed and Feed Rates
Adjusting machining speeds and feed rates ensures that the brass does not overheat. A slower feed rate can reduce the heat generated, leading to a better finish and preventing damage to the material.
Design for Machinability
When designing parts for CNC machining, consider the brass’s properties. Implementing rounded edges and avoiding features that would require excessive material removal can significantly improve the machining process, making it easier and more efficient.
Common Issues in CNC Machining of Brass
Tool Wear and Failure
As mentioned earlier, tool wear can be significantly affected if the brass is not maintained below its melting point during machining. Understanding the nuances can guide how to adjust the machining parameters.
Solution: Regular Inspection and Replacement of Tools
Having a robust inspection program and scheduling regular tool replacements can help mitigate this issue.
Dimensional Inaccuracy
Brass tends to soften if subjected to high temperatures for too long. As a result, dimensions can be compromised.
Solution: Employ Temperature Control
Using integrated CNC systems that monitor temperature and adjust settings on the fly can ensure that temperatures stay within acceptable limits.
Surface Finish Quality
Poor surface finish can stem from exceeding the melting point of brass, leading to a decreased quality of the final product.
Solution: Fine-tune Machining Parameters
Optimizing speed, feed rates, and tool types will significantly contribute to improvement in surface finish quality.
Case Studies
Case Study 1: C36000 Brass in Aerospace Parts
A manufacturer specializing in aerospace components faced challenges in getting precise dimensions in their CNC machined C36000 brass parts. A review of their process revealed that excessive temperatures from high feed rates were causing softening and dimensional inaccuracy.
After implementing a cooling system and adjusting feed rates, the manufacturer achieved precise dimensions and improved production efficiency by over 30%.
Case Study 2: Plumbing Fixtures
A plumbing fixture manufacturer was dealing with surface finish issues. It was found that the improper selection of tooling was causing excessive heat generation. By switching to carbide tools and refining speeds and feeds, they enhanced their surface finishes and gained customer satisfaction.
Understanding the relationship between melted brass properties and CNC machining is a vital aspect of the manufacturing process that should not be overlooked. Focusing on temperature control, tooling selection, and design for machinability are foundational techniques that can significantly enhance part quality and improve overall efficiency.
In addition, by implementing best practices in machining parameters and regular inspections, manufacturers can reduce costs, minimize waste, and maximize product quality.
Ultimately, the lessons learned from this exploration of brass properties offer essential insights for engineers and manufacturers alike. As industries continue to demand higher precision and efficiency, grasping these principles will be crucial for success. If you’re involved in CNC machining processes, it’s time to rethink your strategies concerning material properties. Remember that leveraging brass’s unique characteristics can lead to extraordinary results in your machining endeavors.
Continuing to explore and adapt your understanding of how materials behave under various conditions can not only optimize your current processes but also pave the way for future innovations in manufacturing. Understanding and applying these principles is not just valuable; it’s essential for thriving in the competitive world of CNC machining.






