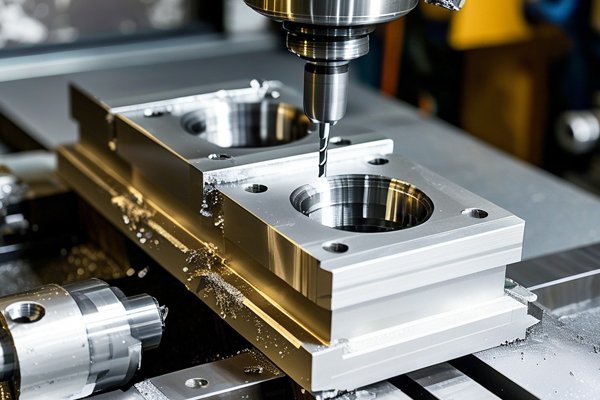
Did you know that the precision of CNC machined components can be the difference between a flawless product and a complete mechanical failure? If you think about the countless applications of aluminum—ranging from aerospace to automotive and even consumer electronics—it’s astonishing to realize that even a minor deviation in dimensions can lead to significant issues down the line. This blog delves deep into how CNC (Computer Numerical Control) aluminum processing plants guarantee dimensional consistency in aluminum parts, exploring the challenges, methodologies, and advanced technologies employed to achieve high levels of accuracy.
Understanding the Importance of Dimensional Consistency
Dimensional consistency refers to the ability to maintain specific measurements across multiple parts produced through a manufacturing process. In industries where precision is non-negotiable, such as aerospace, medical devices, and high-performance automotive components, achieving this consistency is critical.
Even the slightest variations can result in:
Given these implications, CNC aluminum processing plants employ a plethora of strategies to ensure dimensional consistency, from sophisticated technologies to rigorous quality control measures.
The Role of Advanced CNC Machinery
Modern CNC machinery is equipped with high-precision tools optimized for machining aluminum. These tools undergo rigorous testing and calibration to ensure they consistently deliver precise results.
A. Tool Geometry and Materials
The design and material of the cutting tools play a significant role in maintaining dimensional consistency. Tools made from high-speed steel (HSS), carbide, and ceramic are typically used for their durability and ability to maintain sharp edges. The right geometry ensures effective cutting while minimizing thermal distortion and tool wear.
Today’s CNC machines integrate sophisticated control systems that allow for real-time adjustments and monitoring.
A. Feedback Loops
These systems often incorporate feedback loops that can detect deviations from desired specifications in real-time. If a tool begins to dull or a machine experiences an unexpected vibration, these systems can automatically adjust parameters to correct any issues before they impact the final product.
B. Adaptive Machining
Adaptive machining is an advanced feature in many modern CNC systems. It allows the machining process to automatically adapt based on real-time data and analytics, refining parameters like cutting speed and feed rate to achieve better results continuously.
Importance of Material Selection and Preparation
Different aluminum alloys exhibit varying behavior during machining and use. Selecting the appropriate alloy not only affects the part’s mechanical properties but also how it machines.
A. Understanding Alloys
For instance, 6061 aluminum is versatile and widely used due to its excellent mechanical properties and weldability. On the other hand, 7075 aluminum offers superior strength but is more challenging to machine. Making informed decisions about alloy selection plays a crucial role in achieving consistent dimen
sional tolerances.
Before machining, aluminum must be properly prepared. This can involve:
Proper material preparation can drastically reduce variability in machining outcomes.
Rigorous Quality Control Processes
Quality control is integral to ensuring dimensional consistency in CNC aluminum processing. Here are some of the principal methods employed:
SPC involves using statistical methods to monitor and control the manufacturing process.
A. Process Capability Indices
Measurements such as Cp and Cpk are used to determine how capable a process is of producing parts within specified limits. By continually analyzing these indices, manufacturers can adjust processes proactively rather than reactively.
Many CNC plants incorporate in-process inspection systems that use sensors and gauges to ensure parts conform to specifications while being machined.
A. Laser Scanning and Probe Inspection
Advanced technologies like laser scanning and touch probes can measure geometric dimensions without interrupting the machining process. These measurements provide immediate feedback, allowing operators to make on-the-fly adjustments to maintain tolerances.
After machining, parts undergo exhaustive quality checks to ensure that every piece meets strict specifications.
A. Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM)
CMMs are frequently used to perform dimensional inspections and are crucial in high-precision industries. They measure the physical geometrical characteristics of an object and can compare the part against predefined specifications with incredible accuracy.
Employee Training and Skill Development
While technology plays a critical role in ensuring dimensional consistency, the expertise of operators is irreplaceable. CNC operators must be well-trained in:
Continuous education programs, certifications, and hands-on training enable CNC personnel to sharpen their skills and maintain high production standards.
Continuous Improvement Through Technology
CNC machining is not static; it evolves as new technologies emerge. Processing plants increasingly adopt Industry 4.0 principles, which emphasize connectivity, data analysis, and automation.
Integrating IoT devices allows the collection of data from machines throughout the production process. Analyzing this data can uncover inefficiencies, leading to continuous refinement of production standards.
AI can play a transformative role in production environments by predicting machine failure, optimizing tool paths, and suggesting adjustments to improve consistency.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Dimensional Consistency Techniques
Case Study 1: Aerospace Component Manufacturer
An aerospace company implemented rigorous SPC and integrated CMMs into their workflow. They achieved a dramatic reduction in part rejection rates by monitoring process capabilities and conducting real-time inspections.
Case Study 2: Automotive Parts Supplier
A leading automotive parts supplier improved dimensional consistency by investing in adaptive machining technology. Their ability to make instant changes based on live data led to a significant reduction in machining errors, pushing their part accuracy levels to new heights.
In summary, ensuring dimensional consistency in CNC aluminum processing is paramount for producing high-quality components in various industries. Through the application of advanced machining tools, state-of-the-art control systems, meticulous quality assurance, employee training, and continuous improvement technologies, CNC aluminum processing plants can achieve exceptional dimensional accuracy.
This blog underscores the importance of investing in proper technologies and process enhancements to maintain dimensional integrity. In a world where precision can mean the difference between success and failure, manufacturers must prioritize developing and implementing effective strategies for dimensional consistency. As industries evolve, staying ahead of technological advancements and continuously refining processes will become increasingly crucial in achieving operational excellence and satisfaction for clients and end-users alike.
Understanding these elements is not just beneficial; it is essential for anyone involved in the manufacturing and CNC machining industries, ensuring products meet high standards and perform reliably in their applications.






