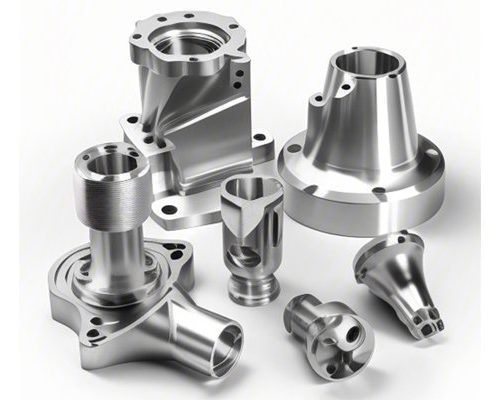
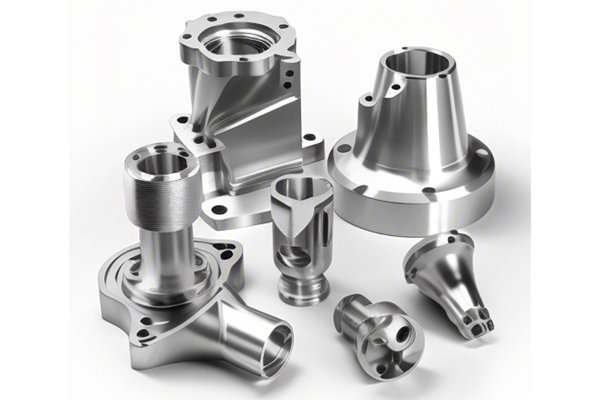
In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining has emerged as a cornerstone technology that streamlines the production of precision components across numerous industries. At the forefront of this technological revolution is YL Machining, a name synonymous with quality and efficiency in CNC machining solutions. In this expansive exploration, we delve into the specifics of CNC machining for two vital materials—ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) and Polyurethane (PU)—focusing particularly on their applications in seals.
As the need for durability, flexibility, and precision becomes increasingly paramount, understanding how CNC machining affects these materials can empower manufacturers and facilitate informed decisions. Let us embark on a journey through the intricate world of CNC machining, unveiling the nuanced advantages, challenges, and best practices.
—
The Fundamentals of CNC Machining
What is CNC Machining?
CNC machining is an automated manufacturing process that utilizes computer-controlled machines to create exact and intricate parts. From a digital model designed using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software, a CNC machine interprets the instructions through G-code, guiding the cutting tools with remarkable precision.
Advantages of CNC Machining
—
Understanding ABS and Polyurethane (PU)
What is ABS?
ABS is a thermoplastic polymer that is widely used due to its strength, rigidity, and ease of processing. Characterized by its good impact resistance and toughness, ABS is commonly found in consumer goods, automotive components, and appliances.
Applications of ABS
In the realm of seals, ABS provides a reliable barrier against moisture and contaminants. Given its moldability and affordability, ABS is a favored choice in applications that require both functionality and cost-efficiency.
What is Polyurethane (PU)?
Polyurethane is a versatile polymer that can be produced in either rigid or flexible forms. Known for its exceptional abrasion resistance and flexibility, PU materials can adapt to various environments, making them suitable for dynamic seals subjected to significant stress and wear.
Applications of PU
PU seals are prevalent in automotive, aerospace, and construction applications due to their high resilience and adaptability. They can endure various temperatures and mechanical stress factors, making them more advantageous in conditions where flexibility is crucial.
—
The CNC Machining Process for ABS and PU Seals
Material Selection
Choosing the Right Material: When determining whether to use ABS or PU for seals, factors like environmental exposure, required durability, and budget come into play.
Cost Analysis: ABS tends to be more cost-effective for projects that prioritize quantity over flexibility, whereas PU may incur higher costs but deliver superior performance in demanding applications.
Tool Selection and Cutting Parameters
Machining Techniques
Quality Control Measures
Post-Processing Techniques
—
Challenges in CNC Machining of ABS and PU Seals
Material Characteristics:
Tool Wear: Due to the composite nature of PU, tool wear may be accelerated and require frequent changes of cutting tools.
Waste Material: Managing waste production is essential for cost efficiency, necessitating careful design and machining strategy.
—
Best Practices for CNC Machining ABS and PU Seals
—
As we come to the end of our exploration into the intricacies of CNC machining ABS and PU for seals, it becomes evident that success in this field is a symphony of precision, material understanding, and adaptive strategies. At YL Machining, we pride ourselves in harnessing both cutting-edge technology and profound expertise to deliver top-of-the-line machining solutions that cater to our clients’ unique needs.
By comprehensively understanding the interplay of materials, techniques, and best practices, manufacturers are better equipped to innovate and lead in their respective fields. Whether you lean toward the robustness of ABS or the dynamic flexibility of PU, CNC machining stands as the bridge that transforms raw ideas into finely engineered realities.
Let us not only embrace the complexities of this technology but also harness them—not just for today, but for the future of manufacturing. The possibilities are limitless when we utilize our creativity, technology, and expertise.
Call to Action
For anyone looking to elevate their CNC machining projects, reach out to YL Machining today. Together, let’s explore the endless possibilities of precision engineering that can redefine what’s achievable in your industry!



